Table of contents
1. What is implantation bleeding?
2. Is implantation bleeding common during early pregnancy?
3. How long after implantation bleeding can I test?
4. Signs of successful implantation
5. Choosing the right test
6. Conclusion
Medically reviewed by Sarah Montagu (NPs, SRH). Sarah is a highly-qualified sexual and reproductive health nurse with 15+ years of experience.
Illustrated by Sabrina Bezerra, Erin Rommel & Maria Papazova
Pregnancy can be a difficult journey to navigate, and for many women & AFAB individuals, the early signs of pregnancy can be both thrilling and nerve-wracking as they eagerly await confirmation of this life-changing event.
Among many pregnancy symptoms, implantation bleeding may be something a person experiences after recently becoming pregnant. Though it is often mistaken for the start of a light period, this light spotting may be the sign of successful implantation.
In this article, we'll dive into the intricate details of implantation bleeding, its significance in the early stages of pregnancy, and the optimal timing for that all-important pregnancy test. So, if you're looking for answers and peace of mind on your journey to parenthood, read on to uncover the key insights that will help you navigate this exciting phase with confidence and clarity.

What is implantation bleeding?
Implantation bleeding is light bleeding that occurs during the early stage of pregnancy. It is characterised by light spotting or discharge that can range in colour from pink to brown.
Implantation bleeding is caused when a fertilised egg attaches to the uterine wall during conception. As the egg travels down the fallopian tube and implants into the uterine lining, small amounts of bleeding can occur.
This light bleeding typically occurs around the same time your period is due to begin. It's because of this that many of us can mistake implantation bleeding for a light period, resulting in many patients not realising they're pregnant at first.
Is implantation bleeding common during early pregnancy?
If you’re trying to get pregnant, noticing a bit of blood can send you into a mini panic. But rest assured, experiencing implantation bleeding is a common occurrence after conception.
Around 15-25% of people experience implantation bleeding during the first trimester. However, it's important to keep in mind that while implantation bleeding is relatively common, it's not a guaranteed occurrence in every pregnancy.
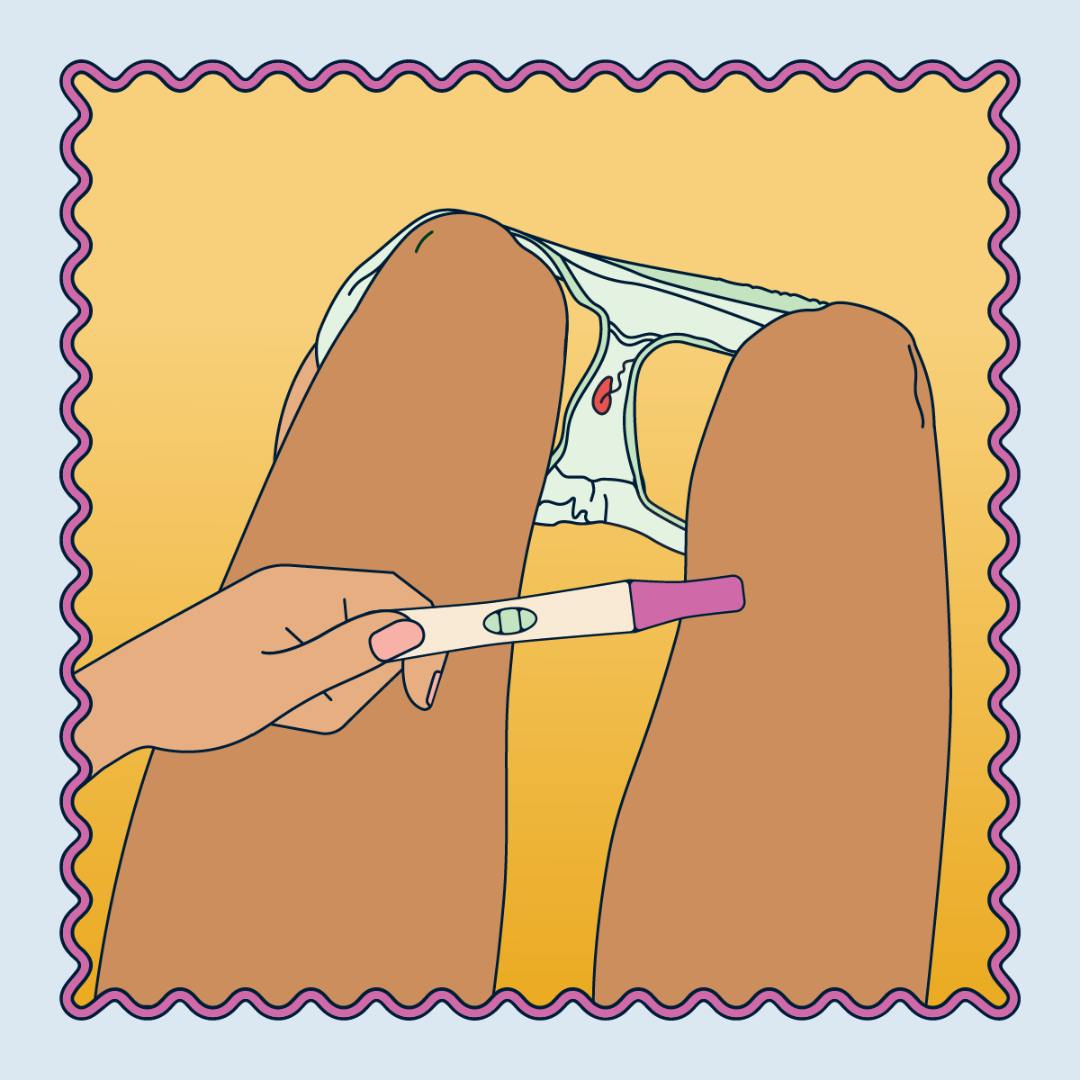
How long after implantation bleeding can I test?
The timing of when to take a pregnancy test after implantation bleeding largely depends on the sensitivity of the test and the accuracy you desire. Generally, you should wait at least a few days to a week after implantation bleeding before taking a test for the most reliable results. Here's a rough guideline:
Early Detection Tests
Some pregnancy tests are designed for early detection and can provide accurate results as early as 7-10 days after conception. This means you can potentially test a few days after implantation bleeding and receive a positive result.
Standard Home Pregnancy Tests
Home pregnancy tests detect the hormone hCG in your urine, and these tests are the most common method that women use to find out if they are pregnant. This stands for human chorionic gonadotropin, which is a hormone produced during pregnancy.
It is often referred to as the "pregnancy hormone" because its levels in the body increase significantly shortly after a fertilised egg attaches to the uterine lining (implantation) and continues to rise throughout early pregnancy.
From the moment implantation occurs, your body begins releasing hCG into your system. For a positive pregnancy test, hCG levels must be above 25mUI/mL and it can take a week before the hCG levels in your system reach this level that is then able to be detected by a home pregnancy test.
It's because of this that it's really, really important to remember that testing too early can result in false negative pregnancy tests. It's natural to want to take a pregnancy test the moment you notice any implantation bleeding, but doing this does increase the likelihood that you will receive a false negative.
Alternatively, wait until you're past the expected date of your period. This gives your body enough time to release the hCG levels and as such, provide a positive pregnancy test result.
Blood Tests
If you want the most accurate and earliest confirmation of pregnancy, consider a blood test. Blood tests can detect hGC levels in the blood as early as 3-4 days after implantation, with this being one of the quickest and reliable ways to yield a positive result.
Signs of successful implantation
There are a few important signs to look out for that indicate that you have experienced a successful implantation. As we've mentioned, implantation bleeding or light spotting can be a sign of successful implantation. However, there are also other signs including:
- Cramping
- Implantation bleeding
- Sore breasts
- Increased basal temperature
- Frequent urination
- Missed period
As we've mentioned, not every woman experiences the same pregnancy symptoms. That means it's important to be vigilant of any unusual changes to your body, from light implantation cramps to needing to use the toilet more frequently. It's important to point out that these cramps may be a lot less intense than your typical period cramps, and whilst there isn't any medical evidence that these are a sign of early pregnancy, many women say they experience light implantation cramps.
Choosing the right test
The choice of which pregnancy test to use depends on your preference and how early you want to know if you're pregnant. If you can't wait and want to test as soon as possible after implantation bleeding, an early detection urine test or a quantitative blood test may be your best options.
However, keep in mind that even the most sensitive tests can sometimes yield false negatives if taken too early. For the most accurate results, consider waiting a few days longer if you receive a negative result.
Also, while our at-home vaginal screening test can’t tell you if you’re pregnant, it’s a great way to identify microbes that may make it harder to conceive or reduce the likelihood of IVF success. With this, you can better understand your fertility and what is right for your body.
Conclusion
Implantation bleeding can be an early sign of pregnancy, but unfortunately it can also be confused with your regular period. The only way to know for sure is to wait the appropriate amount of time and take a test. Whilst a home pregnancy test is the most common method of testing, it's important to remember that taking a urine pregnancy test too soon can produce a false negative.
If you’re trying to conceive, looking after your vaginal microbiome is essential. Our ProViotics can help you to stay on top of maintaining strong levels of friendly lactobacilli. With our ProViotics, you can help ward off any unwanted infections and create a healthier, happier vaginal microbiome that supports your fertility and overall health.
And lastly, don't forget, if you're experiencing any unusual symptoms, pain (particulary shoulder tip pain) that feels different to normal or something that just doesn't seem or feel quite right, always seek professional medical advice.






